Data-Centric Hardware Security
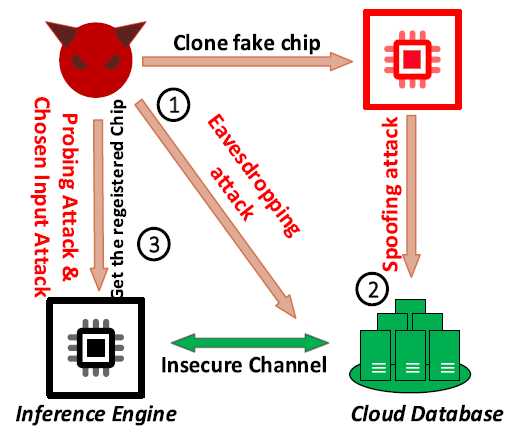
In memory-centric AI engines, neural network parameters are stored close to or inside memory arrays. These model parameters are regarded as valuable assets considering the expensive resources put into the training process. The coupling of memory and computing leaves the valuable data vulnerable to security threats such as eavesdropping, spoofing, probing attacks, and adversarial input-output pair gathering. Thus, novel memory circuit and system designs are necessary to address these rising security concerns.
Research Directions:
- Novel memory bitcell and array configurations for data security
- ML-based attacks on memory-centric computing and their security solutions
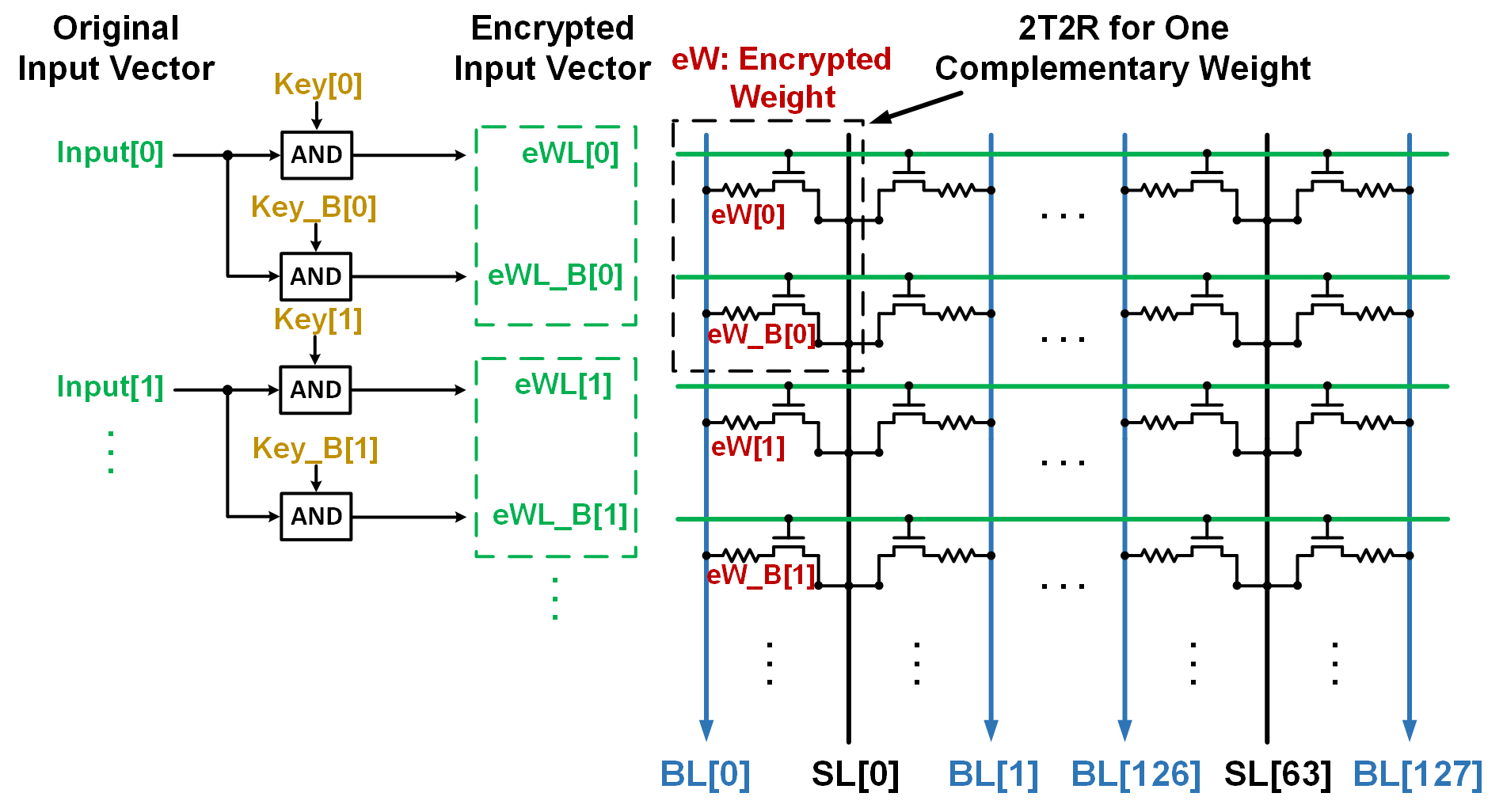
To enhance the hardware security of in-memory computing AI engines, we have devised an encryption scheme to provide effective protection of on-chip weights stored in non-volatile memories. We apply embedded encryption to the memory array by mapping each weight onto a bitline using complementary 2T2R bitcell, where one row will contain the true bits and the other row will contain dummy bits. This technique allows valuable DNN models to be distributed in this encrypted format to authorized users, who will be provided with a key to decrypt the true bit rows.